(a)
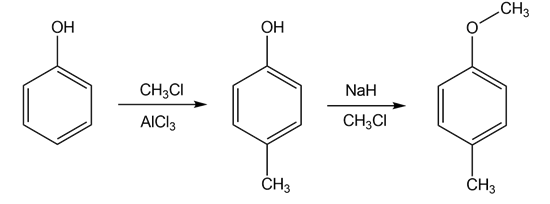
- Phenol reacts with methyl chloride in presence of Lewis acid to give 4-methyl phenol.
4-methyl phenol reacts with NaH in presence of methyl bromide to give 4-methyl-anisole
Step 1
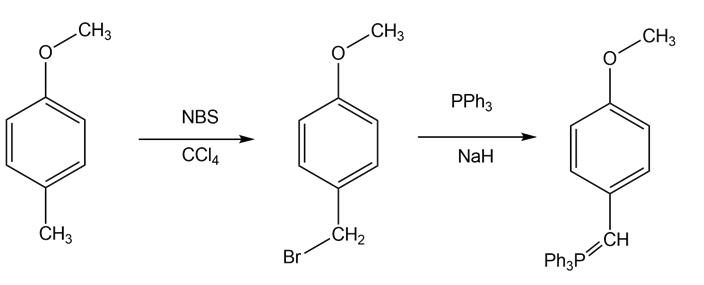
- 4-methyl anisole reacts with NBS (N-Bromosuccinimide) in the presence of carbon tetrachloride to give 1-(bromomethyl)-4-methoxybenzene 1-(bromomethyl)-4-methoxybenzene reacts with triphenylphosphine in the presence of NaH to give a Wittig reagent
Step 2
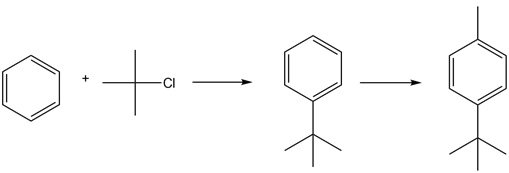
- Benzene reacts with 2-chloro-2-methylpropane in the presence of Lewis acid to give tert-butyl benzene.
Tert-butyl benzene reacts with methyl chloride in the presence of Lewis acid to give 1-(tert- butyl)-4-methylbenzene
Step 3
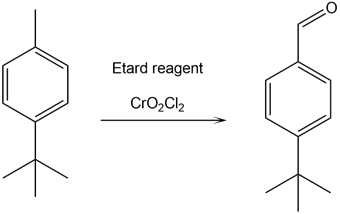
- 1-(tert-butyl)-4-methylbenzene reacts with Etard reagent to give 4-(tert-butyl) benzaldehyde.
Step 4
- The Wittig reaction between 4-(tert-butyl) benzaldehyde and a Wittig reagent (form step 2) give both cis and trans isomers of compound (a)
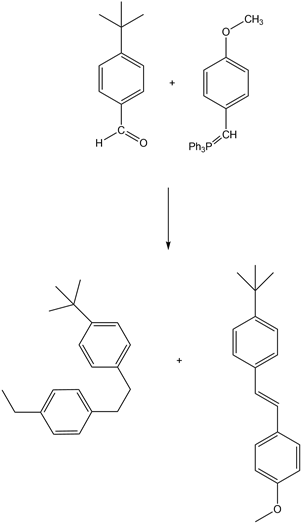
Step 5
(b)
- The carbonyl group of the ketone is protected using 1,2-ethanediol in the presence of acid.
Alcohol reacts with PBr3 to give alkyl bromide
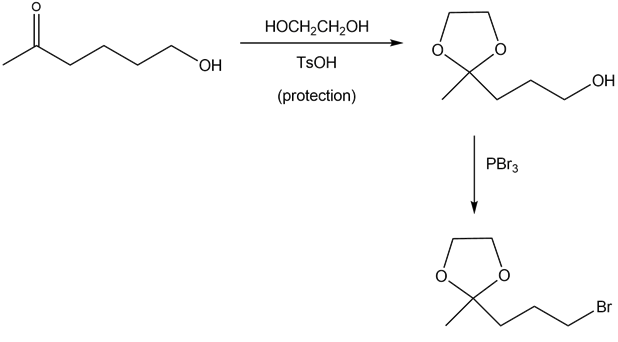
Step 1
- Alkyl bromides react with Mg in presence of dry ether to give Grignard reagent.
2-propanol undergoes oxidation with PCC to give 2-propanone Grignard reagents react with 2-propanone in presence of water to give a tertiary alcohol.
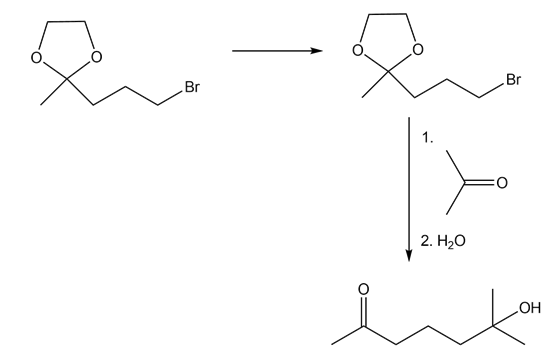
Step 2
c)
- Benzene reacts with isobutyryl chloride in the presence of lewis acid to give 2-methyl-1-phenylpropan-1-one.
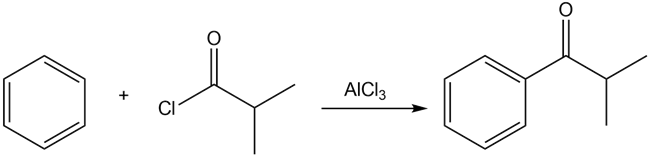
Step 1
- 2-methyl-1-phenylpropan-1-one reacts with diethyl amine to give desired compound N, N-diethyl-2-methyl-1-phenylprop-1-en-1-amine.
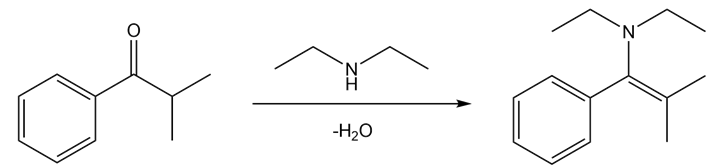
Step 2






























