Nitration happens when one (or more) of the hydrogen atoms on the benzene ring is replaced by a nitro group. Benzene is treated with a mixture of concentrated nitric acid and concentrated sulphuric acid at high temperature. During nitration, a nitronium ion is formed when nitric acid undergoes a reaction with sulfuric acid. Nitronium serves as an electrophile which is attacked by the nucleophilic benzene ring. Resulting product of nitration is nitrobenzene.
In part (d), toluene on reaction with potassium permanganate gives benzoic acid which on nitration results in product in which nitro group is at meta position to the carboxylic group due to directive influence of carboxylic group. Further, on reduction with iron and hydrogen chloride, required product is obtained.
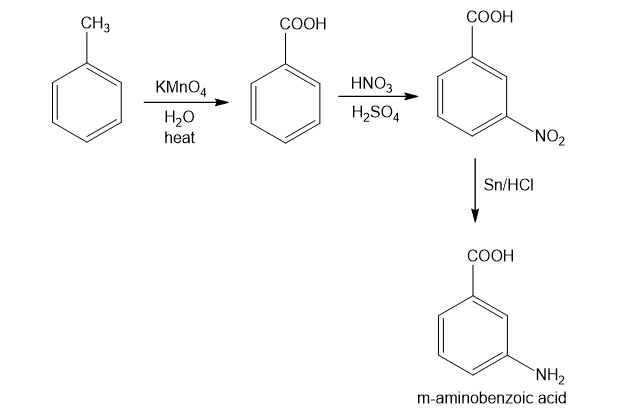
Formation of the required product


















