Peptides often have functional groups other than free amino groups at the N terminus and other than carboxyl groups at the C terminus.
(a) A tetrapeptide is hydrolyzed by heating with 6 M![]() , and the hydrolysate is found to contain Ala, Phe, Val, and Glu. When the hydrolysate is neutralized, the odor of ammonia is detected. Explain where this ammonia might have been incorporated in the original peptide.
, and the hydrolysate is found to contain Ala, Phe, Val, and Glu. When the hydrolysate is neutralized, the odor of ammonia is detected. Explain where this ammonia might have been incorporated in the original peptide.
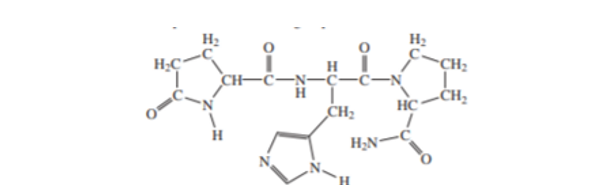
(b) The tripeptide thyrotropic hormone releasing factor(TRF) has the full name pyroglutamylhistidylprolinamide. The structure appears here. Explain the functional groups at the N terminus and at the C terminus.
(c)On acidic hydrolysis, an unknown pentapeptide gives glycine, alanine, valine, leucine and isoleucine. No odor of ammonia is detected when the hydrolysate is neutralized. Reaction with phenyl isothiocyanate followed by mild hydrolysis gives nophenylthiohydantoin derivative. Incubation with carboxypeptidase has no effect. Explain these findings.







