(a)
The structure of the compound can be drawn as:
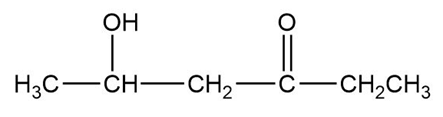
Structure of Compound
In this organic compound, one hydroxy group is present at the fifth carbon atom and the ketone functional group is attached to the third carbon atom.Therefore, the IUPAC name of the compound is and the common name is .
(b)
The structure of the compound can be drawn as:
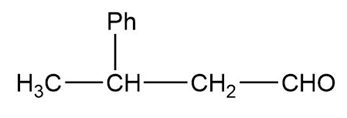
Structure of Compound
In this organic compound, one phenyl group is present at the third carbon atom and the aldehyde functional group is attached to the first carbon atom. Therefore, the IUPAC name of the compound is and the common name is .
(c)
The structure of the compound is given as:
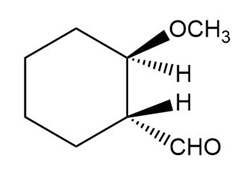
Structure of Compound
The IUPAC name of the compound is
(d)
The structure of the compound is given as:
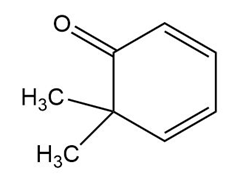
Structure of Compound
In this organic compound, two methyl groups are present at the sixth carbon atom and the ketone functional group is attached to the first carbon atom. Also, two double bonds are present at the second and fourth carbon atoms respectively. Therefore, the IUPAC name of the compound is .

















