The functional group of five heterocyclic bases in nucleic acids may be hydrogen bond acceptor A, a hydrogen bond donor D, or both A/D.
In heterocyclic bases, amine groups could serve either as hydrogen bond acceptors by using non-bonding electrons on nitrogen or as hydrogen bond donors by using a hydrogen bond to the nitrogen.
The A, D, and A/D designations show that the maximum numbers o hydrogen bonds forming between bases are two hydrogen bonds between thymine and adenine and three between cytosine and guanine.
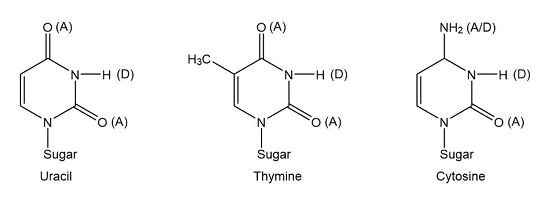
Pyrimidine based heterocyclic bases
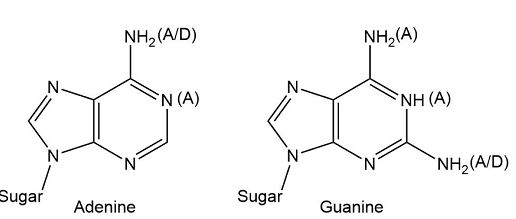
Purine based heterocyclic bases





