Ascorbic acid (vitamin C) reacts with according to the equation
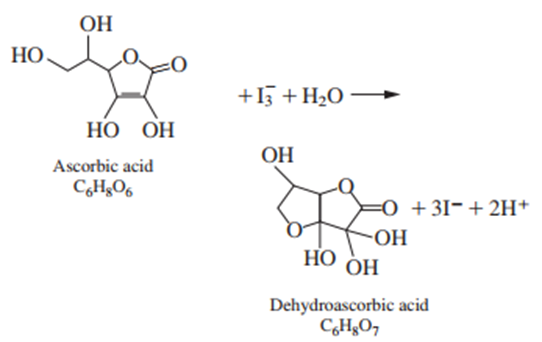
Starch is used as an indicator in the reaction. The end point is marked by the appearance of a deep blue starch-iodine complex when the first fraction of a drop of unreacted remains in the solution.
(a) Verify that the structures above have the chemical formulas written beneath them. You must be able to locate every atom in the formula. Use atomic masses from the periodic table on the inside cover of this book to find the formula mass of ascorbic acid.
(b) If 29.41 mL of solution are required to react with 0.197 0 g of pure ascorbic acid, what is the molarity of thesolution?
(c) A vitamin C tablet containing ascorbic acid plus inert binder was ground to a powder, and 0.424 2 g was titrated by 31.63 mL of . Find the weight percent of ascorbic acid in the tablet.



