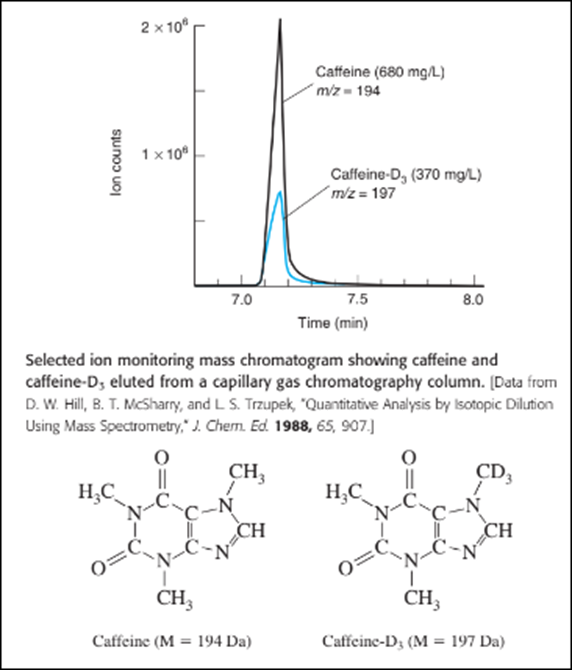
Quantitative analysis by selected ion monitoring. Caffeine in beverages and urine can be measured by adding caffeine- as an internal standard and using selected ion monitoring to measure each compound by gas chromatography. The figure shows mass chromatograms of caffeine (m/z,194)and caffeine-D, which have nearly the same retention time.
Suppose that the following data were obtained for standard mixtures:
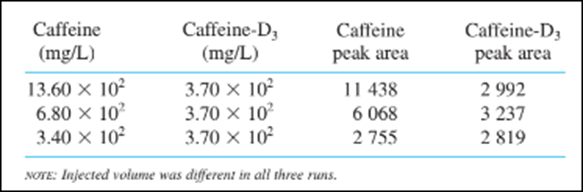
(a) Compute the mean response factor in the equation
role="math" localid="1664874599903"
(b) For analysis of a cola beverage, 1.000mL of beverage was treated with of standard solution containing 1.11 g/Lcaffeine- in methanol. The combined solution was passed through a solid-phase extraction cartridge that retains caffeine. Polar solutes were washed off with water. Then the caffeine was washed off the cartridge with an organic solvent and the solvent was evaporated to dryness. The residue was dissolved in of methanol for gas chromatography. Peak areas were 1144 for m/z197 and 1733 for m/z194. Find the concentration of caffeine (mg/L ) in the beverage.




