Consider the following diagram, which depicts a country with no government expenditure, taxes, or net exports. Answer the following questions and explain your responses using the information in the diagram.
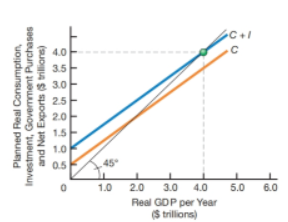
a. What is the marginal saving propensity?
a. What is the current level of projected investment spending over the next few years?
c. What is the current period's equilibrium level of real GDP?
d. What is the current period's saving equilibrium level?
e. What will the change in equilibrium real GDP be if planned investment spending for the current period is increased bybillion? What will the new real GDP equilibrium level be if all other variables, including the price level, remain constant?


