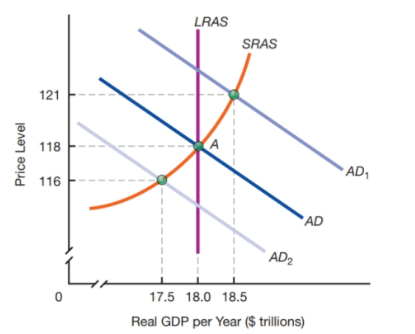
Suppose that, initially, the U.S. economy was in an aggregate demand-aggregate supply equilibrium at point A along with the aggregate demand curve AD in the diagram below. Now, however, the value of the U.S. dollar suddenly appreciates relative to foreign currencies. This appreciation happens to have no measurable effects on either the short-run or the long-run aggregate supply curve in the United States. It does, however, influence U.S. aggregate demand.
a. Explain in your own words how the dollar appreciation will affect net export expenditures in the United States.
b. Of the alternative aggregate demand curves depicted in the figure- versus which could represent the aggregate demand effect of the U.S. dollar's appreciation? What effects does the appreciation have on real GDP and the price level?
c. What policy action might the Federal Reserve take to prevent the dollar's appreciation from affecting equilibrium real GDP in the short run?