The figure below shows the supply curve for tennis balls, S1, for Drop Volley Tennis, a producer of tennis equipment. Use the figure and the table below to give your answers to the following questions.
a. Use the figure to fill in the quantity supplied on supply curve S1 for each price in the following table.
b. If production costs were to increase, the quantities supplied at each price would be as shown by the third column of the table (“S2 Quantity Supplied”). Use those data to draw supply curve S2 on the same graph as supply curve S1.
c. In the fourth column of the table, enter the amount by which the quantity supplied at each price changes due to the increase in product costs. (Use positive numbers for increases and negative numbers for decreases.)
d. Did the increase in production costs cause a “decrease in supply” or a “decrease in quantity supplied?” Explain.
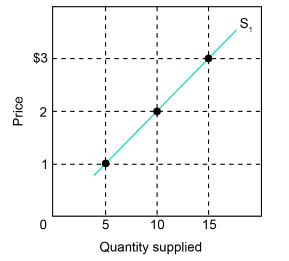
| Price($) | S1
Quantity Supplied | S2
Quantity
Supplied | Change in Quantity Supplied (S2-S1) |
| 3 | - | 4 | - |
| 2 | - | 2 | - |
| 1 | - | 0 | - |





