Efficiency losses are possible even if the suppliers are willing to produce and sell a product. The supplier can supply a good above or below the equilibrium level, which can result in inefficiency.
The diagram below shows the optimal level of output:
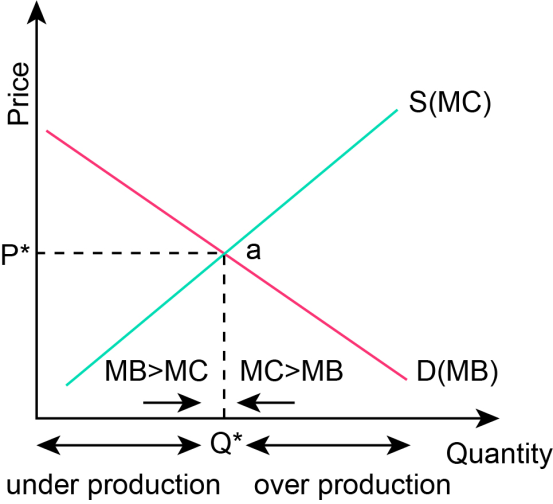
You can see the following points:
- Underproduction happens when the output produced is below the optimal level of output Q* (value to buyers > cost to sellers).
- Overproduction happens when the output produced is above the Q* level (cost to sellers > value to buyers).
At these points, the output is not produced by all the producers who have minimum costs and not consumed by all the buyers who value the good higher than the cost.
Efficiency losses can occur due to both underproduction and overproduction and not just one of the mentioned.





