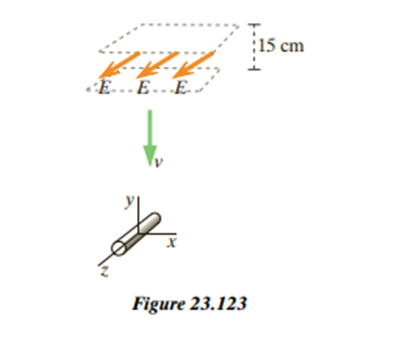
A slab (pulse) of electromagnetic radiation that is 15cm thick is propagating downward (in the direction) toward a short horizontal copper wire located at the origin and oriented parallel to the z axis, as shown in Figure 23.123. (a) The direction of the electric field inside the slab is out of the page (in the direction). On a diagram, show and describe clearly the direction of the magnetic field inside the slab.
(b) You stand on the x axis at location, at right angles to the direction of propagation of the pulse. Your friend stands on the z axis at location. The pulse passes the copper wire at time , and at a later time you observe new nonzero electric and magnetic fields at your location, but your friend does not. Explain. What is ? (Give a numerical answer.) How long a time do these new fields last for you? (c) On a diagram, show and describe clearly the directions of these new nonzero fields ( and ) at your location. Explain briefly but carefully.