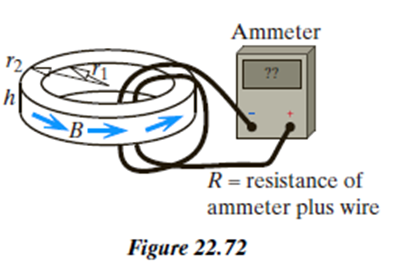
In Figure 22.72 a toroid has a rectangular cross section with an inner radius , an outer radius , and a height , and it is wrapped around by many densely packed turns of current-carrying wire (not shown in the diagram). The direction of the magnetic field inside the windings is shown on the diagram. There is essentially no magnetic field outside the windings. A wire is connected to a sensitive ammeter as shown.
The resistance of the wire and ammeter is .
The current in the windings of the toroid is varied so that the magnetic field inside the windings, averaged over the cross section, varies with time as shown in Figure 22.73:
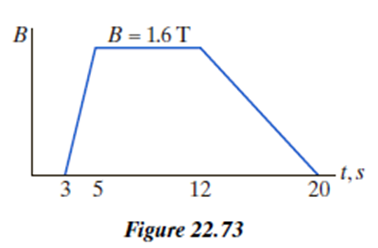
Make a careful graph of the ammeter reading, including sign, as a function of time. Label your graph, and explain the numerical aspects of the graph, including signs.




