Consider the given data as below.
The length of both strings L=50 cm
The mass of upper is
The mass of lower ball is
The initial height of the ball is
The angular momentum of the simple pendulum with small amplitude is calculated as
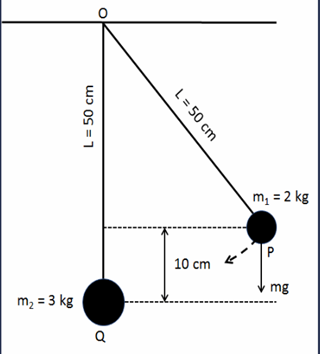
The potential energy converted in kinetic energy at the point of maximum speed
Consider before collision the speed of massisand the speed of mass is and after collision the speed of mass is and the speed of mass is . So according to law of conservation of mass,
Before collision:
After collision:
Than
Now the maximum displacement after collision the kinetic energy converted into potential energy so
From calculated as
Hence, the maximum displacement after collision is
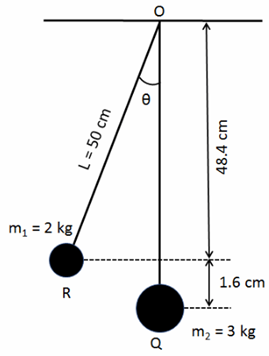
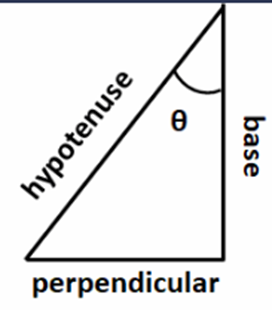
Now calculated the angular displacement,
Hence, the frequency and maximum angular displacement of the motion after the collision is f =0.7 Hz and respectively





